Trump’s Reciprocal Tariffs: Assessing the Impact on India’s Economy

Trump’s Reciprocal Tariffs: Assessing the Impact on India’s Economy
The imposition of reciprocal tariffs by the U.S. could make Indian products less competitive in the American market due to increased costs.
In a significant shift in U.S. trade policy, President Donald Trump announced the implementation of reciprocal tariffs on countries imposing higher duties on American imports, with the new measures set to take effect from April 2, 2025.
This move aims to address what the administration perceives as unfair trade practices, particularly targeting nations like India, China, and members of the European Union.
Understanding Reciprocal Tariffs
Reciprocal tariffs are designed to mirror the tariffs that other countries impose on U.S. goods. For instance, if a country levies a 25% tariff on American products, the U.S. would impose an equivalent 25% tariff on imports from that nation.
President Trump emphasized that this approach seeks to establish a “level playing field” for American businesses, asserting that many countries have long benefited from trade imbalances at the expense of the United States.
India’s Position in Global Tariff Structures
India has historically maintained relatively high tariff rates to protect its burgeoning industries and safeguard employment. Sectors such as agriculture, automobiles, and electronics have been shielded through these protective measures.
However, these high tariffs have been a point of contention in international trade discussions, with the U.S. and other nations advocating for reduced barriers to enhance market access.
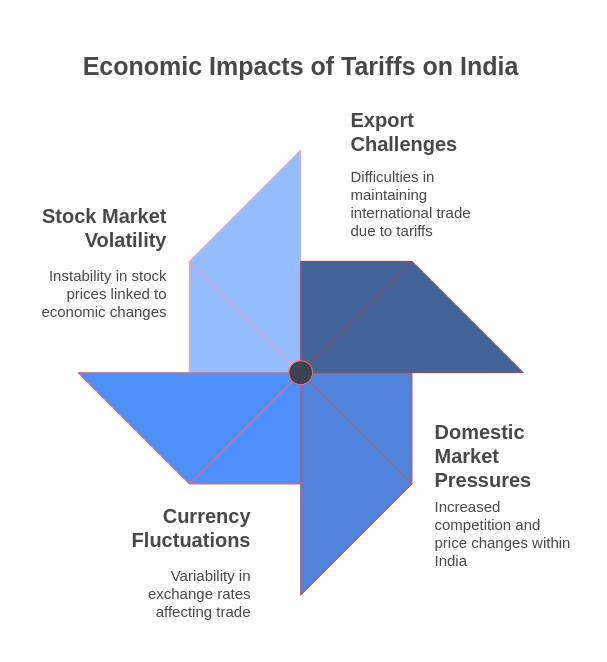
Potential Impacts on India’s Economy
Export Challenges: The imposition of reciprocal tariffs by the U.S. could make Indian products less competitive in the American market due to increased costs.
Key sectors like textiles, pharmaceuticals, and information technology services, which have significant export volumes to the U.S., might experience reduced demand, affecting revenue and employment.
Domestic Market Pressures: With decreased access to the U.S. market, Indian exporters may redirect their products domestically, potentially leading to an oversupply. This shift could result in price reductions and strain profit margins for local businesses.
Currency Fluctuations: Trade tensions and uncertainties could exert downward pressure on the Indian rupee. Analysts anticipate that concerns over a potential trade war and a slowing domestic economy might lead to a steeper slide of the rupee against the U.S. dollar in the coming year.
Stock Market Volatility: The announcement of U.S. tariffs has already led to fluctuations in Indian stock markets. Investors are wary of the potential negative impacts on export-driven companies, leading to a cautious trading environment.
Government and Industry Responses
In light of these developments, Indian officials are actively engaging in diplomatic discussions to mitigate potential adverse effects. Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal has initiated talks with U.S. counterparts, aiming to negotiate terms that could alleviate the impact of the tariffs.
Additionally, India is pursuing trade agreements with other global partners, including the European Union and the United Kingdom, to diversify its export markets and reduce dependency on any single economy.
Industry leaders are also advocating for strategic measures to enhance competitiveness. Investments in technology, innovation, and quality improvements are being emphasized to ensure that Indian products remain attractive globally, despite potential tariff barriers.
Global Trade Dynamics
The U.S.’s move towards reciprocal tariffs marks a notable shift in global trade dynamics, signaling a more protectionist stance. This approach could prompt other nations to adopt similar measures, potentially leading to a cycle of retaliatory tariffs. Such a scenario might disrupt global supply chains, increase costs for consumers, and slow down economic growth worldwide.
Looking Ahead
As the implementation date for the U.S. reciprocal tariffs approaches, it is crucial for India to adapt to the evolving trade landscape. Diversifying export markets, enhancing product competitiveness, and engaging in proactive diplomatic negotiations will be essential strategies to navigate the challenges posed by these new trade policies.
While the immediate impacts may present hurdles, they also offer an opportunity for India to reassess and strengthen its position in the global economy. By focusing on innovation, quality, and strategic partnerships, India can work towards mitigating the adverse effects of the tariffs and continue its trajectory of economic growth.
Acknowledgement: This news story has been developed with inputs from ChatGPT, which has sourced information from different media reports.